

- #HOW TO CHECK MAC ADDRESS ON CENTOS 6 HOW TO#
- #HOW TO CHECK MAC ADDRESS ON CENTOS 6 FULL#
- #HOW TO CHECK MAC ADDRESS ON CENTOS 6 SOFTWARE#
Amonth other things, it provides the lsb_release command that can help you check CentOS version. Linux Standard Base (LSB) is a joint project by major Linux vendors to standardise configuration and usage of Linux distros. Use lsb_release command to confirm Lunux release Once you browse to the CentOS wikipedia page, just search for the kernel version number and it should find something like this for you, confirming CentOS version to be 7.4-1708: CentOS 7 Release datesĥ.
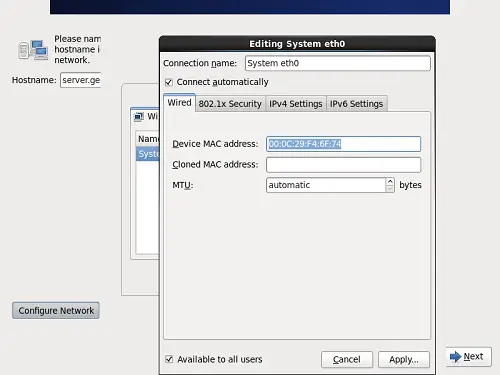
If you want to check the MAC address of some specific network interface then you need to use the interface name with ip link show command and check the MAC address from ether field as shown below.
#HOW TO CHECK MAC ADDRESS ON CENTOS 6 HOW TO#
Using the kernel version number – 3.10.0-693 in my example – you can confirm the CentOS release using one of the public version information pages, like the CentOS wikipedia page. Method 6: How to find an ethernet MAC Address in Linux using ip link show command. There are many ways to confirm your Linux kernel version, like uname command: :~ $ uname -r Confirm CentOS version using Linux kernel version If you’re using RedHat, just do the same for the redhat-release package.
#HOW TO CHECK MAC ADDRESS ON CENTOS 6 FULL#
It will include the exact CentOS release version right in its full package name: :~ $ rpm -qa centos-releaseĬ.x86_64 Next option you have is to use the RPM package manager to query a special package named centos-release. By default, first network interface will start with eth0. Enter network configuration folder, and look for ethx file. Machine ID: 5f7e36c18a974f06ae94ddaaf11d71e8īoot ID: 337e48b00fed4abe9ab929fed5aa6018Īrchitecture: x86-64 3. The following are the tested steps on CentOS 6.4 and may be applied on CentOS 6.5 and CentOS 6.6 operating system. Provided that you’re running a recent enough version of Linux, you should have the hostnamectl command installed.Īmong other things, hostnamectl provides easy access to the OS release information and Linux kernel version: :~ $ hostnamectl 1 root root 14 /etc/redhat-release -> centos-release 2. In fact, if you look at the /etc/redhat-release file on a CentOS server closely, you’ll notice that it is a symbolic link to /etc/centos-release: :~ $ ls -ald /etc/redhat-release That’s okay and the good news is this will still work in CentOS: :~ $ cat /etc/redhat-release Interesting: if you’re coming from RedHat infrastructure, you’d normally be looking for /etc/redhat-release file. Now that we’re sure it’s CentOS, let’s look into the /etc/centos-release file – this will show you the full release version of your operating system: :~ $ cat /etc/centos-release As shown below, it will help you with confirming your Linux distro and its major release version (CentOS and 7 in my case): :~ $ cat /etc/os-release Just to be super sure that you’re actually looking at a CentOS distribution of Linux, I suggest you start with the /etc/os-release file. This article introduces 5 of the most common ways to do just that. With CentOS being a rather popular server grade Linux distro, I can see that many visitors of my blog look for the same guidance quite regularly: check CentOS version.
#HOW TO CHECK MAC ADDRESS ON CENTOS 6 SOFTWARE#
Knowing release helps with highlighting software dependencies and compatibilities, confirms availability of certain features in your OS and simplifies the process of system administration – certain releases have a preferred set of commands for day-to-day management. One of the very first questions a Linux user asks is about confirming the release (OS version) in use.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
